10 Facts About Your Skin
10 Facts About Your Skin
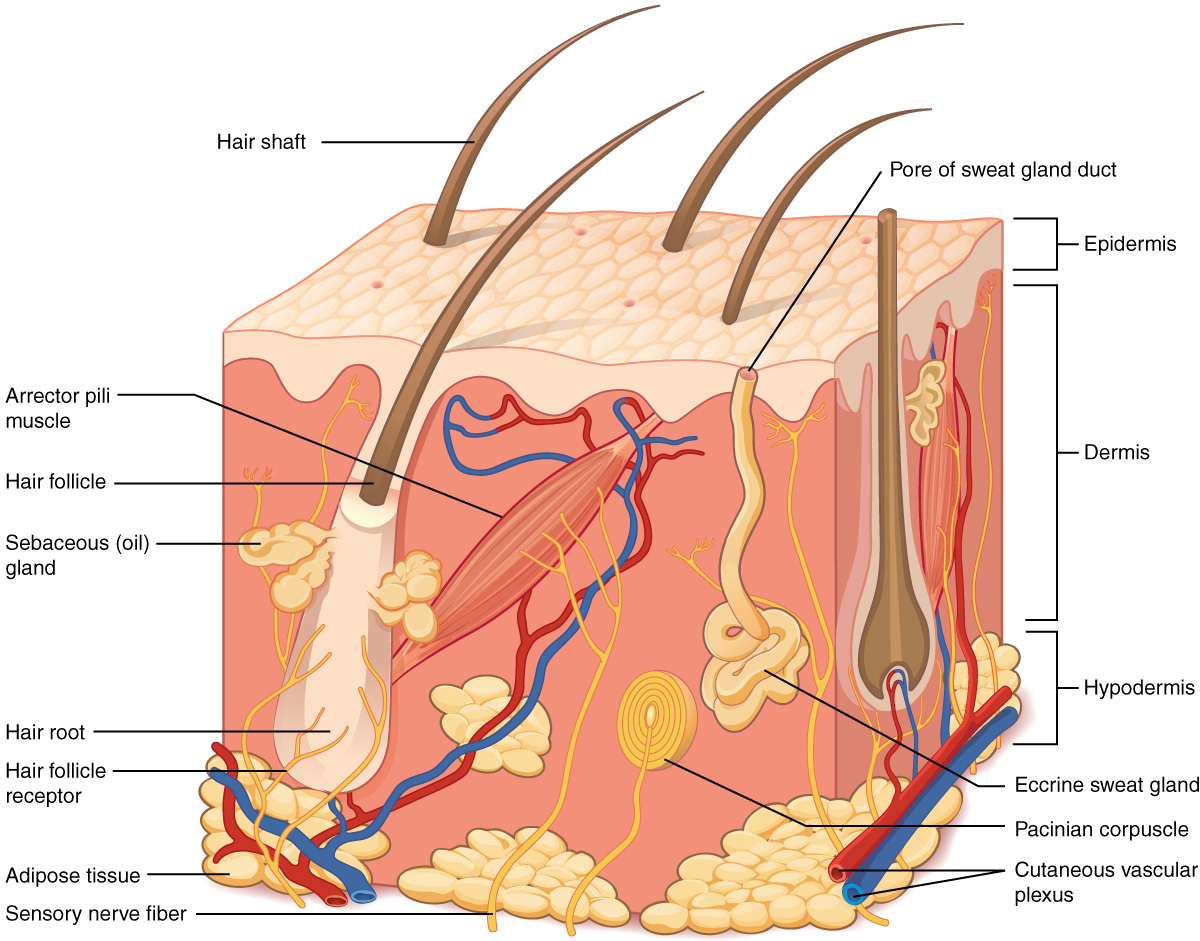
Our Skin has more complexity than it is commonly understood. The skin can renew itself and repair certain types of damage that may contribute to skin cancer. The skin has multiple layers, including the epidermis, the dermis, and the fat under the dermis.
The outermost layer, known as the epidermis, serves as a waterproof barrier that retains moisture while preventing the entry of bacteria, fungi, viruses, allergens, and irritants. This layer houses squamous cells, basal cells, and melanocytes. The epidermis contains dead cells that create a waterproof barrier and melanocytes that produce melanin to protect against UV light. The layer is responsible for the production of melanin, which imparts colour to the skin and hair.
Beneath the epidermis lies the dermis, which contains sweat and oil glands, hair follicles, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels that facilitate waste removal and help regulate body temperature. Cells within this layer generate collagen and elastin fibres, providing structural integrity and elasticity to the skin.
The innermost layer, referred to as the hypodermis or subcutaneous fat layer, consists of fat stored beneath the skin. This fat layer serves as a cushion and insulates the body. When the blood vessels from the dermis extend into the hypodermis, they enlarge to circulate blood, deliver nutrients to other organs, and remove waste.
Factors like age, climate, and temperature can affect the changes in skin type. It is essential to examine the three primary layers that compose it. Skin cancer can occur due to any damage to the DNA within any of these cells.
Let’s know Some Skin Facts!
From top to bottom, the three main layers of skin are the Epidermis, the Dermis and the Hypodermis.
1. 19 million skin cells make a square inch of skin.: The skin is the body's largest organ, covering the entire body. A square inch of skin contains many different types of cells, including melanocytes, keratinocytes, sweat glands, blood vessels, and nerve endings. Every skin cell has its specific job in that inch of skin. About 60,000 melanocyte cells are present that produce melanin pigment, which gives skin its colour. Every human being has melanocytes, except those who are born with albinism. The majority of skin cells are keratinocytes. The two types of cells are basal and squamous cells, from which the most common skin cancers can arise. The average adult has 2,800 square inches of skin, which is about 22 square feet of skin.
2. Your skin sheds 30,000 skin cells in 60 seconds: Every day, 30,000 skin cells get shed off by your body in a minute - the dead, dull skin flakes off your face and body, but it’s not visible to you. It takes around a month for new skin cells to be formed, though this decreases with age. The reason for dull and dry skin after 60 years of age is because Cell turnover takes up to six to eight weeks after the age of 60, which builds up the skin to dull and dry. As people age, their skin becomes thinner, drier, and more fragile. Products that contain retinoids promote new cell growth, or alpha hydroxy acids, glycolic acid can speed up the process (at any age). This loosens up the intercellular glue-like substance. It is the substance that holds skin cells together on the surface and allows them to slough off. These ingredients are in creams, cleansers, lotions or serums.
3. The skin has 11 miles of blood vessels: The blood vessels bring oxygen and nutrients to your cells, remove waste and help regulate your skin’s temperature. Hence, blood vessels help keep skin healthy and radiant. Your blood vessels dilate when the skin gets warm, allowing heat to escape to the outside air. And when the skin is cold outside, blood vessels constrict, maintaining the heat in your skin.
4. Your Skin is 10 to 15 percent of your body weight: It is one of the heaviest of all the organs in your body. 10 to 15 per cent is composed of blood, lymph vessels, collagen, living cells, water, oils, lipids (fats), nutrients, hair follicles, and dead cells. Skin is made of water, protein, fats, and minerals.
5. Skin has its metabolism: Skin also has a metabolism. It is the process within the skin of controlling the production and breaking down the collagen and elastin. The amount of collagen in the body determines how smooth and firm the skin is. Exercising can increase the amount of collagen produced. Your skin renews its cells, repairs the damage caused, and responds to the topical products you are using effectively. But the skin’s metabolic processes lag with age and exposure to environmental aggressors. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation causes changes in cellular metabolism, these changes lead to visible signs of photoaging.
6. Your skin is on the clock: Skin and circadian rhythm: Skin has a circadian rhythm, meaning it has a sense of time. Daylight is for protection, while nighttime is for repair. Researchers have discovered that your skin has a day rhythm. The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the brain governs it. This group of nerve cells acts as a master clock. In daylight hours, your skin acts as a shield and protects your cells from ultraviolet light, pollution, free radicals, etc. Skin’s repair processes start at a higher frequency at night, and research shows that repair peaks at night. The nighttime is the best time to moisturise your skin. The body’s Nucleotide Excision Repair system removes UV photodamage from DNA. This is controlled by the Skin’s circadian rhythm. If this system fails to remove damaged DNA, then these mutations can cause skin cancer. So wearing sunscreen creams during the daytime to protect your skin from UV rays is very important.
7. Skin has a microbiome: The community of microbes present in your intestines is called a microbiome. It includes immunotherapy for melanoma. It influences immune health and how a person will respond to drug treatments. The skin has trillions of microorganisms, making a Microbiome. Microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses and fungi play a crucial role in fighting infection, controlling inflammation and helping your immune system recognize possible threats.
8. Skin is an “emotional” organ: Skin and well-being: Skin can reflect a person's life, with wrinkles, calluses, and rings under the eyes all telling a story. Your skin is the most sensitive organ in your body. It reacts to everything, from temperature to vibration, to pressure, pain and pleasure. The dermis contains cells with nerve fibres. These cells transmit sensations of touch to the brain. Skin is highly reactive to emotional stress. According to experts, stress and skin have a direct connection. Stressful situations trigger hives, itching, and even sweating. Research has shown that inflammatory skin issues such as eczema, psoriasis and acne rise with full-time stress. Stress can exaggerate skin issues, but skin can also send signals to the brain, triggering a stress response.
9. Your skin can flex: Your skin covers not just your muscles but those tiny muscles as well. These tiny muscles are called the arrector pili muscles. They are located in your hair follicles. These little muscles make your hair stand straight up when you get goosebumps.
10. The outermost layer is the Skin’s Protector: Skin protects the body from injury, infection, heat, and light. It also regulates body temperature, stores fat and water, and helps produce vitamin D. The outermost layer acts as a barrier to protect the skin. Sunscreen helps in keeping the skin's surface safe from sunburns and protects its cells from damage from UV. It helps in keeping the moisture locked inside the skin and potential irritants, allergens and bacteria out of the skin. When due to UV ray exposure, harsh cleansers, and over-exfoliation, the skin’s microscopic tears that are formed get damaged. This makes water escape and gives potential irritants a fast pass into your skin. Which makes the skin dry and sensitive.


