SKIN CANCER
SKIN CANCER
Things to Know About Cancers of the Skin
What Is Skin Cancer? Cancer that forms in the tissues of the skin is called skin cancer. There are several types of skin cancer. Skin cancer that forms in neuroendocrine cells (cells that release hormones in response to signals from the nervous system) is called neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin. Skin cancer that forms in squamous cells (flat cells that form the surface of the skin) is called squamous cell carcinoma. Skin cancer that forms in melanocytes (skin cells that make pigment) is called melanoma. Skin cancer in the lower part of the epidermis (the outer layer of the skin) is called basal cell carcinoma. Most skin cancers form in older people on parts of the body exposed to the sun or in people with weakened immune systems. Skin cancer is the out-of-control growth of abnormal cells in the epidermis, the outermost skin layer, caused by unrepaired DNA damage that triggers mutations. These mutations lead the skin cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumours. The main types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer. The main types of skin cancer are squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Melanoma is much less common than the other types but much more likely to invade nearby tissue and spread to other parts of the body. Most deaths from skin cancer are caused by melanoma. Explore the links on this page to learn more about skin cancer prevention, screening, treatment, statistics, research, clinical trials, and more. Skin cancer may be common, but it’s still dangerous. Early detection is crucial, and it helps to know what to look for to find it. Spotting any warning signs of skin cancer improves your outlook and leads to a better response with treatment.
ANATOMY OF THE SKIN
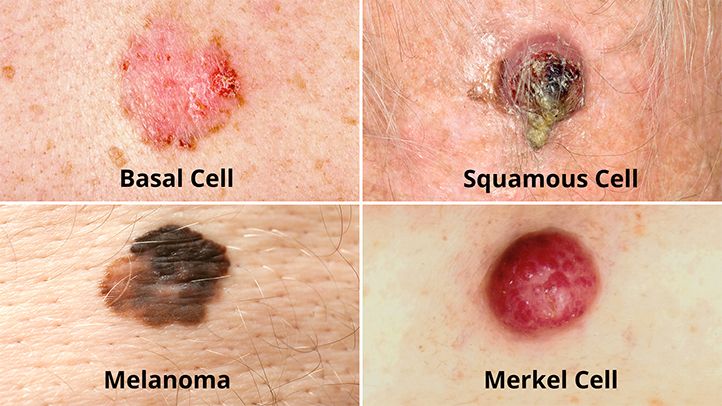
Q1. What Does Skin Cancer Look Like? , Skin cancers can look quite different from one person to another due to skin tone, size type of skin cancer and location on the body.
Q2. What Causes Cancers of the Skin? The two main causes of skin cancer are the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays and using UV tanning beds. The good news is that if skin cancer is caught early, your dermatologist can treat it with little or no scarring and high odds of eliminating it. Often, the doctor may even detect the growth at a precancerous stage, before it has become a full-blown skin cancer or penetrated below the surface of the skin.
Q3. Do I need to get yearly checks for skin cancer?
The simple answer is yes. Many types of skin cancer are curable if caught early. Melanoma, a form of skin cancer, can quickly spread to other body parts. You should check yourself regularly for any changes in your skin, moles or spots that have changed, or new growths. If you find any irregularities, schedule an appointment with your doctor. Because skin cancer can develop anywhere on the body, an annual exam with a dermatologist can ensure you do not miss a hard-to-examine area, like the back. The cancer screening process only takes about 20 minutes and can be critical in early detection.
Q4. Does sunburn increase my chance of skin cancer?
Everyone should apply sunscreen daily, even if they are not planning to spend a day in the sun. If you are caught without it and develop sunburn, you may wonder if it increases your chance of skin cancer. Sunburn damages the skin, but it does not cause cancer. However, repeated sunburn and overexposure to the UVB rays from sunlight can weaken skin cells and make them more susceptible to cancer.
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA
Q1. What is Basal cell carcinoma? Basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) are abnormal, uncontrolled growths that arise from the skin’s basal cells in the outermost layer of skin (epidermis).
Q2. What causes it? Most BCCs are caused by the combination of intermittent, intense exposure and cumulative, long-term exposure to UV radiation from the sun.
Q3. How many people get it? BCC is the most common form of skin cancer, with approximately 3.6 million cases diagnosed in the United States each year.
Q4. How serious is it? BCCs can be locally destructive if not detected and treated early. Occasionally, these cancers metastasize (spread), and in very rare instances, they can be fatal.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Q1. What is Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)? SCC is an uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells arising from the squamous cells in the outermost layer of skin (epidermis).
Q2. Where is it usually found? SCCs are common on sun-exposed areas such as the ears, face, scalp, neck and hands. These are places where the skin often reveals signs of sun damage, including wrinkles and age spots.
Q3. What causes it? Cumulative, long-term exposure to UV radiation from the sun and tanning beds causes most SCCs.
Q4. How many people get it? SCC is the second most common form of skin cancer. An estimated 1.8 million cases are diagnosed each year in the U.S.
Q5. How serious is it? SCCs can sometimes grow rapidly and metastasize if not detected and treated early.
Melanoma
Q1. What is Melanoma? Melanoma is a cancer that develops from melanocytes, the skin cells that produce the melanin pigment which gives skin its colour.
Q2. Where is it usually found? Melanomas often resemble moles and sometimes may arise from them. They can appear on any area of the body, even in areas that are not typically exposed to the sun.
Q3. How many people get it? In 2024, an estimated 200,340 new cases of melanoma are expected to occur in the U.S. Of those, 99,700 cases will be in situ (noninvasive), confined to the epidermis (the top layer of skin), and 100,640 cases will be invasive, penetrating the epidermis into the skin’s second layer (the dermis).
Q4. How serious is it? Melanoma is the most dangerous of the three most common forms of skin cancer. Melanomas can be curable when caught and treated early. In 2024, melanoma is projected to cause about 8,290 deaths.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Q1. What is Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC)? MCC is a rare, aggressive skin cancer.
Q2. Where is it usually found? These tumours usually appear as firm, painless lesions or nodules on a sun-exposed area (about half of the time on the head and neck, and frequently on the eyelids).
Q3. What causes it? Usually associated with a virus called the Merkel cell polyomavirus, MCCs most often arise on sun-exposed areas in fair-skinned individuals over age 50.
Q4. How many people get it? About 3,000 new cases of MCC and about 700 deaths from it occur in the U.S. each year, and that is expected to rise.
Q5. How serious is it? MCCs are at high risk of recurring and metastasizing throughout the body, so early detection and treatment are crucial.
If your doctor doesn’t include skin exams as part of your routine health checkup, it is best to perform your own skin check once per month or visit a dermatologist. However, if your gut tells you something isn’t right, it is best to check with your doctor.


