What Number of SPFs Can Protect My Skin Better?
What Number of SPFs Can Protect My Skin Better?
You must have heard that applying sunscreen is indeed an important part of your daily exercise for your body. Whether you step out in the sun or the rain, it's still important to apply sunscreen, but why is it so important? Let us understand that.
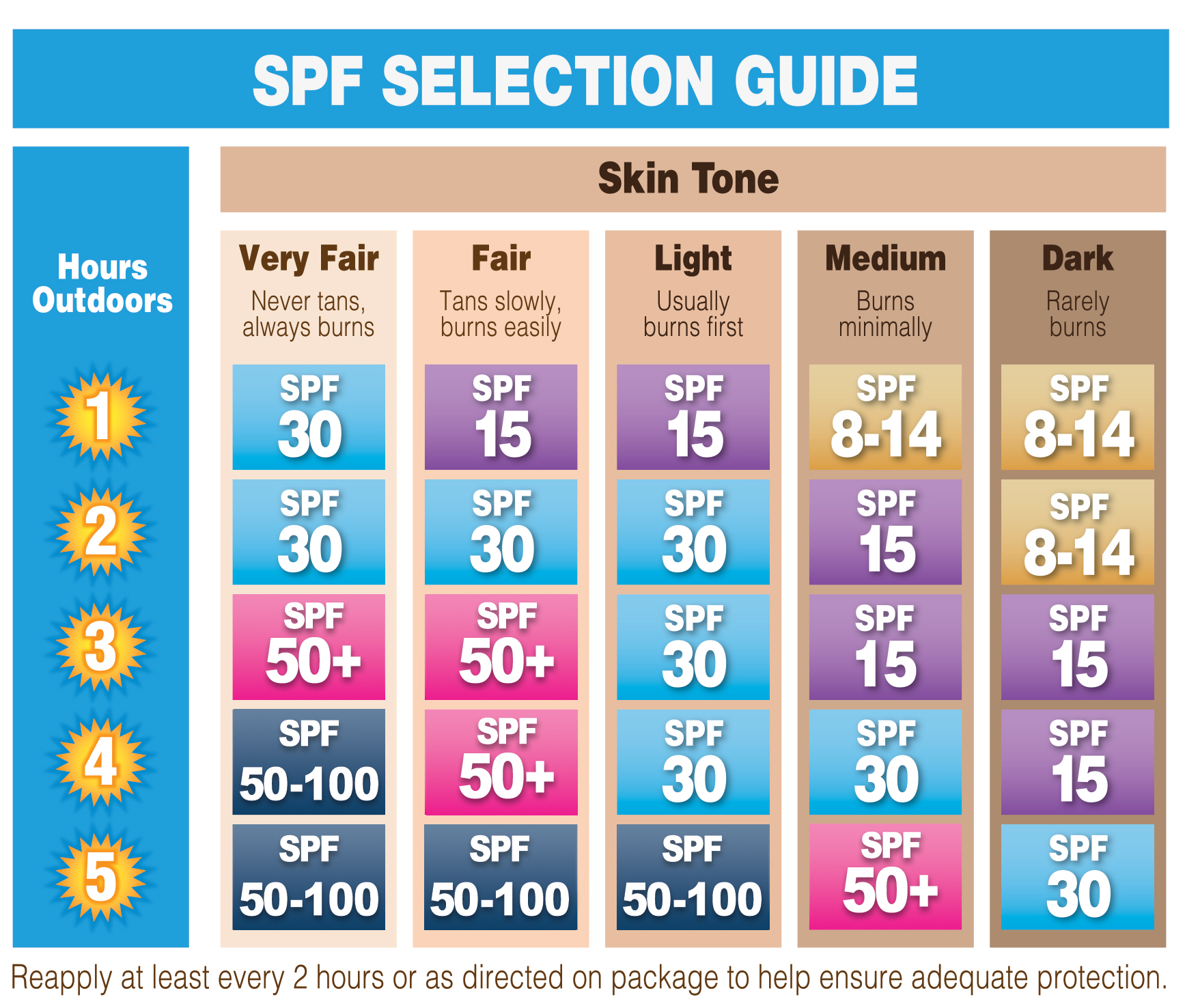
Before you buy sunscreen, it's important to understand what sun protection factor, or SPF, means. SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor, and it measures how well a sunscreen protects your skin from UVB rays. A sunscreen's SPF is a measure of how well it protects you from getting sunburned. The number you see on the bottle when you buy your sunscreen tells you about the safety it can give you from the sun’s Ultraviolet radiation.
SPF measures the amount of solar energy (UV radiation) needed for sunburn-protected skin compared to unprotected skin. A higher SPF value means better sunburn protection. A higher SPF value means that a sunscreen provides greater protection against sunburn, indicating that it takes significantly longer time for your skin to burn when using that sunscreen compared to not using any sunscreen at all; essentially, the higher the SPF, the more UV rays are blocked by the product.
Here are some important things to know about SPF:
- Meaning of SPF: SPF stands for "Sun Protection Factor", it measures how much solar energy (UV radiation) is needed for sunburn-protected skin compared to unprotected skin.
- How SPF works: SPF is not directly related to the time of solar exposure. An SPF 30 sunscreen means it would take 30 times longer for your skin to burn with the sunscreen applied compared to without it. For example, if you normally get sunburned in one hour, an SPF 15 sunscreen doesn't mean you can stay in the sun for 15 hours without burning. Instead, it means SPF 15 sunscreen blocks 93% of UVB rays and allows about 7% of the sun's rays to reach your skin. It means that if you can normally stay in the sun for 10 minutes without burning, SPF 15 sunscreen would allow you to stay in the sun for about 150 minutes without burning.
- Protection level: For best protection, experts recommend using a minimum SPF of 15, applying the proper amount, and reapplying every 2 hours. While a higher SPF indicates more protection, most experts recommend using an SPF of 30 or higher for optimal sun protection.
- SPF levels: SPF 15 blocks 93% of UVB rays, SPF 30 blocks 97% of UVB rays, and SPF 50 blocks 98% of UVB rays.
- Sun protection: Sun protection can help protect you from skin cancer, slow down signs of ageing, reduce the chances of developing hyperpigmentation, and help prevent sunburns.
Everyone should use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every day, irrespective of any weather season, and also regardless of age, gender, or skin type.
The recommended amount of sunscreen to apply is about one ounce to cover your entire body. This is the recommendation from the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AAD) and the Skin Cancer Foundation. Apply enough sunscreen to cover all skin not covered by clothing. Most adults need about 1 ounce to fully cover their body. Don't forget to apply it to the tops of your feet, your neck, your ears, and all your face. Apply sunscreen to dry skin 15 minutes before going out in the sun.
You must apply sunscreen evenly all over your body daily, and if you are going out in the Sun, to protect yourself from the harmful ultraviolet radiations, you should reapply sunscreen to areas that aren't covered by clothing, like your hands, neck, ears, and lips.
In addition to sunscreen, you can also use sun-protective clothing, hats, and umbrellas. The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends sun-protective clothing with at least UPF 30. Sunscreen protects against both UVB and UVA rays. UVA rays can cause skin cancer and ageing.
Ultraviolet light is invisible to humans because it has shorter wavelengths than the light we can see. Within the UV spectrum, two types of rays can damage the DNA in your skin cells and lead to skin cancer. It’s important to protect your skin from both types of radiation, UVB and UVA.
- UVB rays cause sunburn and play an important key role in developing skin cancer. A sunscreen’s SPF number refers mainly to the amount of UVB protection it provides.
- UVA rays cause skin damage that leads to tanning as well as skin ageing and wrinkles. The shortest wavelengths of UVA rays also contribute to sunburn. It’s important to look for the words “broad spectrum” on a product’s label, which means it has ingredients that can protect you from UVA as well as UVB rays.
A sunscreen with higher SPF protection and broad-spectrum coverage offers more protection against sunburn, UVA damage and DNA damage than comparable products with lower SPF values.
The SPF number tells you how long the sun’s UV radiation would take to redden your skin when using the product exactly as directed versus the amount of time without any sunscreen. So, ideally, with SPF 30, it would take you 30 times longer to burn than if you weren’t wearing sunscreen.
An SPF 30 allows about 3 per cent of UVB rays to hit your skin. An SPF of 50 allows about 2 per cent of those rays through. That may seem like a small difference until you realize that SPF 30 is allowing 50 per cent more UV radiation into your skin.
For people who have a history of or high risk of skin cancer, genetic diseases or certain immune disorders, SPF 50 may not be enough.
The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends a water-resistant, broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for any extended outdoor activity. Regardless of the SPF, though, it’s important to apply one ounce (two tablespoons) 30 minutes before going outside and reapply it every two hours or immediately after swimming or sweating.
It’s important not to rely on high-SPF sunscreens alone. No single method of sun defence can protect your skin completely. Sunscreen is just one vital part of a strategy that should also include seeking shade and covering up with clothing, including UV-blocking sunglasses to protect your eyes from the harmful radiations of the sun.


